The Importance of Airway Clearance in Respiratory Health
- Published on:
The Importance of Airway Clearance in Respiratory Health
- Published on:

On this page

The management of bronchial secretions is a key challenge across a wide range of medical conditions, including respiratory disorders, neuromuscular diseases, and patients recovering from thoracic or abdominal surgery. Many acute and chronic respiratory diseases are associated with retained airway secretions due to increased mucus production, impaired mucociliary transport, or an ineffective cough.
Airway Clearance Techniques (ACTs) encompass a variety of strategies designed to assist in the removal of excess secretions from the lungs. Despite the availability of numerous treatment options, there is limited conclusive evidence proving the efficacy of specific techniques across different clinical scenarios. Furthermore, no single ACT has been demonstrated to be superior to others, yet both clinicians and patients recognise the significant burden that retained secretions can impose on respiratory health (1)
Standard respiratory care includes routine efforts to facilitate mucus clearance, with respiratory therapists dedicating a considerable portion of their time to airway management. This blog will explore ACTs such as PEP therapy and cough assist and aim to provide a deeper understanding of their mechanisms, applications, and benefits.
Why is Airway Clearance Important?
Airway Clearance Techniques
Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) Therapy
The goal of PEP therapy is to direct air past the blockage during inhalation, helping to push more air behind the mucus to aid its removal and assist with lung expansion. There are many different devices on the market designed to provide PEP therapy. Some combine PEP with high-frequency oscillations of the airflow, Oscillatory PEP (OPEP). The PEP therapy most used in clinical practice is the low-pressure type (also referred to as “low PEP”). It consists of maintaining a relatively low expiratory pressure in the mouth, between 10 and 20 cmH2O, which we will be discussing below.
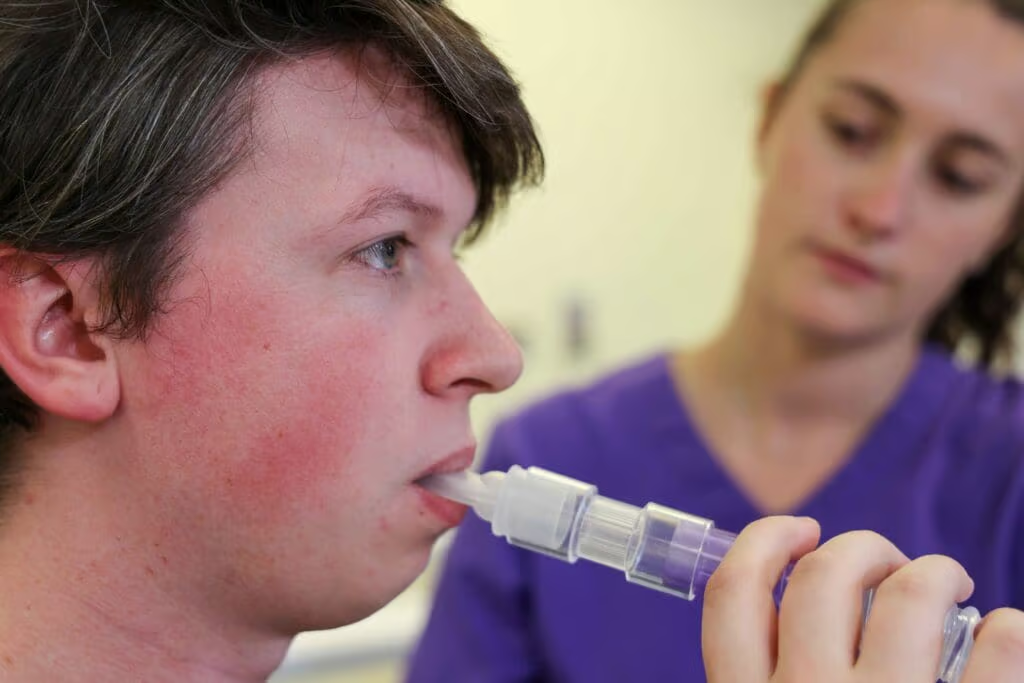
How PEP therapy works
Resistance to Exhalation: The PEP device provides resistance during exhalation. When a patient exhales through the device, they must blow out against a predetermined level of resistance. This resistance can be adjusted depending on the device and the needs of the patient.
Increased Airway Pressure: The resistance creates positive pressure in the airways during exhalation. This positive pressure helps to keep the airways open, preventing them from collapsing and facilitating better airflow through the smaller airways and into the alveoli (air sacs in the lungs).
Mucus Clearance: The positive pressure also helps to mobilise and loosen mucus in the airways. By preventing airway collapse and promoting airflow, it aids in the movement of mucus towards the larger airways, from where it can be more easily coughed out.
Lung Expansion: The process helps to improve lung volumes by encouraging deeper breaths and promoting better distribution of air within the lungs. This can lead to improved oxygenation and overall lung function. (3)
PEP therapy is particularly beneficial for patients with:
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Bronchiectasis
- Chronic Bronchitis
- Postoperative Pulmonary Complications (4)
- Respiratory infections with increased mucus production
Coughing is a vital defence mechanism for lung health, consisting of three phases: inspiratory, compressive, and expiratory. A cough begins with a deep breath in. The glottis (the opening at the top of the voice box) closes, allowing the pressure to build up in the lungs. The respiratory muscles contract and the glottis opens, forcing air back out of the lungs.
It prevents pulmonary aspiration, promotes ciliary activity, and clears airway debris. In patients with weakened respiratory muscles, natural coughing may be insufficient, necessitating the use of cough assist devices.
The devices’ main objective is simply, to stimulate a cough. It applies positive pressure followed by negative pressure across the entire airway, studies have shown this therapy is perhaps the most physiologic mechanical recreation of a natural cough.
AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines 2022 recommend airway techniques such as manual/ventilator hyperinflation which prevents mucus plugging, promotes atelectasis recruitment, and stimulates a cough but can cause a loss of PEEP (4).
Mechanical insufflation-exsufflation (MI-E) is an efficient technique for cough augmentation in ICU respiratory patients, either through an endotracheal tube or through a facial mask. MI-E can be efficient therapy to manage copious secretions and help to avoid reintubation, as well as to improve NIV efficacy in patients that develop respiratory failure after extubation (5).
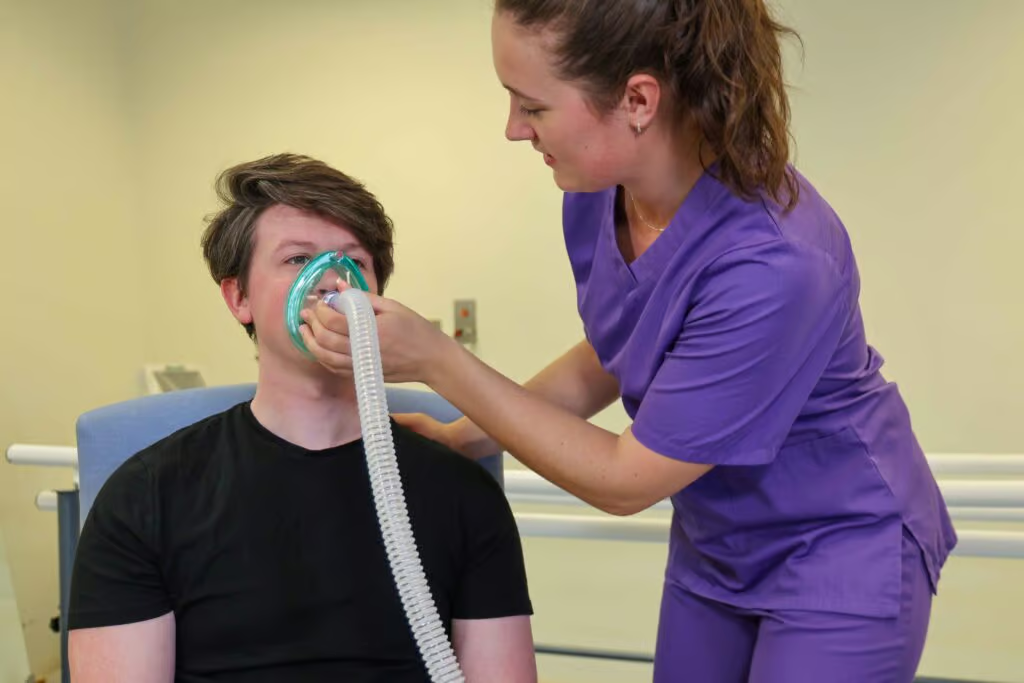
How Cough Assist Works:
- Positive pressure breath in: Expands the lungs and fills them with air.
- Negative pressure breath out: Rapidly removes air, simulating a natural cough.
- Non-invasive application: Can be delivered via mask, mouthpiece, endotracheal, or tracheostomy tube.
Clinical Benefits:
- Enhances secretion clearance by mimicking a natural cough.
- Reduces the need for invasive suctioning.
- Useful for patients with neuromuscular diseases such as muscular dystrophies, spinal cord lesions, motor neuron disease (MND), and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
- Patients recovering from critical illness often experience global muscle weakness, reduced cough strength, and impaired mucociliary clearance. The use of airway clearance techniques can be essential in these cases to prevent complications such as mucus plugging and atelectasis.
Conclusion
Adequate airway clearance is a crucial component of respiratory care, helping to prevent complications associated with retained mucus, such as infection, inflammation, and impaired gas exchange. While a variety of airway clearance techniques exist, including PEP therapy and cough assist devices, no single method is superior for all patients. Individualised treatment plans should be based on a patient’s specific condition, needs, and response to therapy.

Abby Lennon
Clinical Nurse Adviser, RN
Abby works alongside the Clinical Education Team to provide support and education to healthcare professionals using her knowledge and experience as a registered nurse working in respiratory wards and intensive care units over the last eight years.
References
- Airway Clearance Techniques: The Right Choice for the Right Patient – PMC
- Positive expiratory pressure – Common clinical applications and physiological effects – ScienceDirect
- Airway clearance: physiology, pharmacology, techniques, and practice – PubMed
- Chest physiotherapy with positive expiratory pressure breathing after abdominal and thoracic surgery: a systematic review – ÖRMAN – 2010 – Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica – Wiley Online Library
- AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Artificial Airway Suctioning – PubMed
- Effects of mechanical insufflation-exsufflation in preventing respiratory failure after extubation: a randomized controlled trial | Critical Care | Full Text